BIM
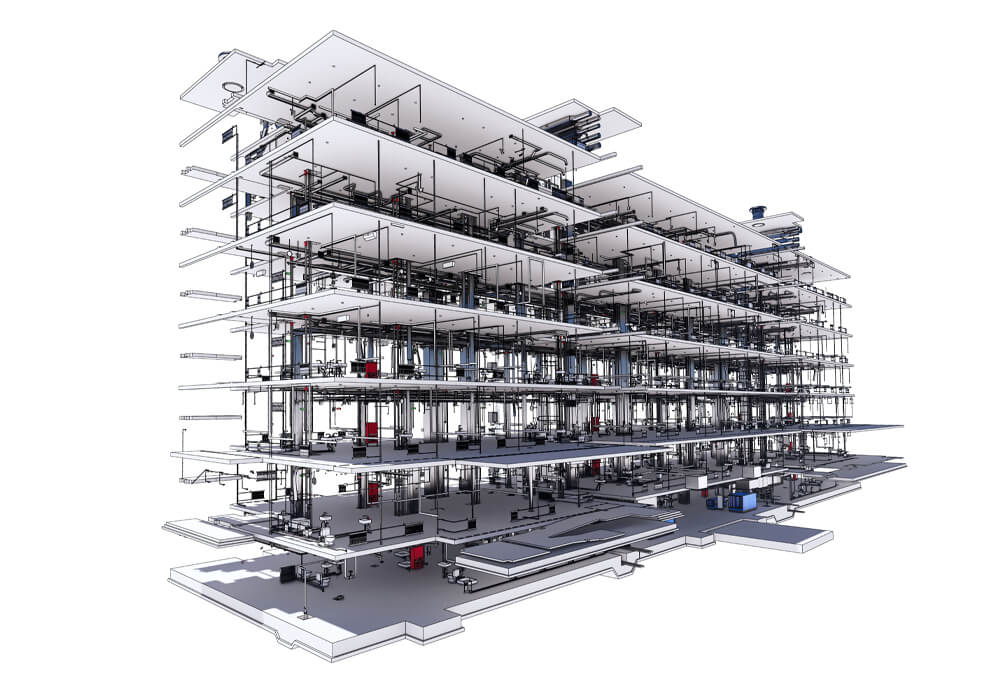

Building Information Modeling (BIM)
P.B.S.M. considers the continuous updating of its technical and professional level to be a central value. For this reason, the team wants to face the challenges of the AECO/FM (Architecture, Engineering, Construction, Operation and Facility Management) sector by making full use of the capabilities of the most innovative methodologies and technologies. One of these is Building Information Modeling (BIM). The BIM methodology focuses on the modeling and management of information relating to the entire life cycle of built assets. P.B.S.M. aims to fully implement this methodology, providing asset information design and management services in compliance with national and international regulatory frameworks. Furthermore, BIM is a necessary professional update following its obligation for public works, as reported in the BIM decree DM 560/2017 and consequent amendments of the Ministerial Decree 312/2021.
Integrated Design
Through BIM, it is created a functional link between the various phases of the life cycle of the works and therefore also of the related professional services, such as planning, design, construction, management, maintenance and dismissal. As reported by the National Building Specification (NBS), BIM consists of the “creation of and information management of a construction project that spans its entire life cycle. As part of this process, a digital and coordinated description of every aspect of the built asset is developed, using appropriate technologies”. This digital description is the federated model of the asset, a congruent and joint set of specialized sub- models that bring together the geometries and information of the various disciplines (architectural, structural, plant engineering, energy model, etc.). On the client’s side, a mature BIM approach provides a service based on structured information models supplied together with all the documentation and documents relating to the asset of interest.

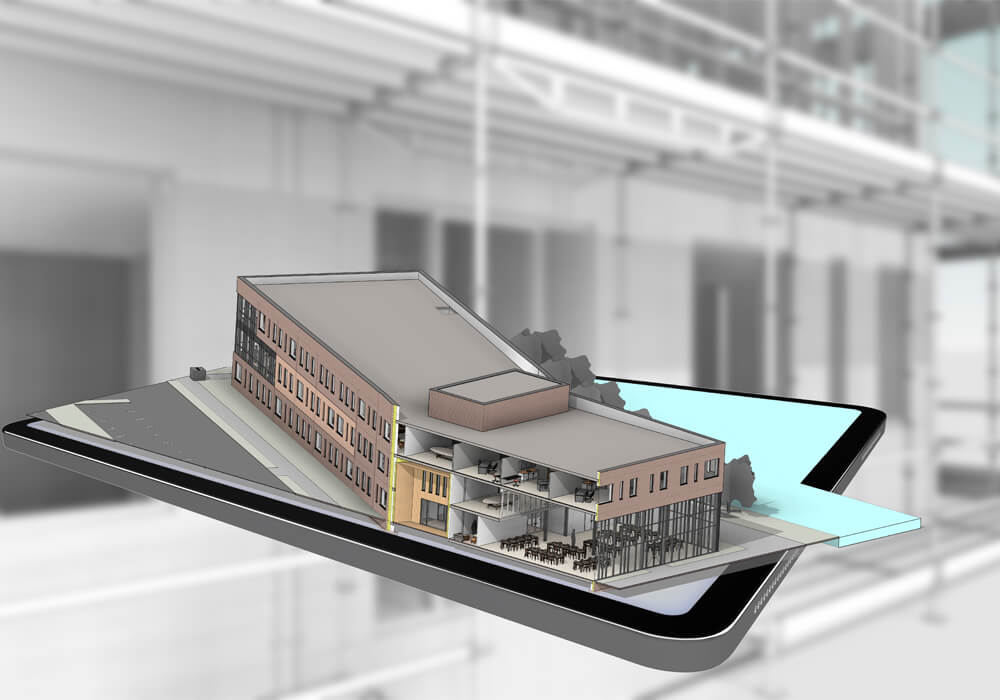
Collaborative Approach
These models serve as a central and authoritative source of information, and over time can be laid as a basis for future services related to the work. For example, the federated model received at the end of a design service can be used by construction companies for site management and monitoring, creating an As-Built model that takes into account the required changes and updates them directly from the final project model. In turn, this model can then be delivered to the manager and maintainer of the work or a subset of it. This allows the creation of durable information, which once consolidated and validated in a certain phase can be resumed without interruption for future services. From the side of those who provide a BIM service, the methodology allows for the establishment of a highly collaborative approach based on standardized processes for verifying, validating and delivering information. This is possible thanks to the wide range of software available to create specialist BIM models and carry out coordination, simulation and/or analysis activities.